Why store solar energy?
Solar photovoltaic generators can generate electricity as long as they are exposed to sunlight. Especially at noon, when the amount of solar radiation is highest, the power generation reaches its highest. However, typical households use electricity primarily in the morning and evening. If all family members are working, the solar power generated at noon often must be fully fed into the grid and cannot meet their own needs. Power storage (also called battery storage) solves this problem and stores the electricity generated during the day in between. In the evening and early morning, if the photovoltaic plant is not producing energy, then it can simply draw electricity from the mains. Energy storage takes its place to meet demand.
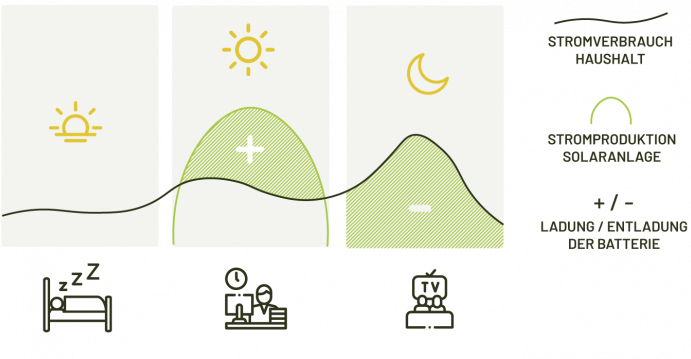
The principle of energy storage power supply
How to increase self-consumption of electricity through electricity storage?
If you install a photovoltaic system in a single-family home, you can use approximately 30% of the solar power yourself. The remaining 70% is fed into the power storage. As energy storage increases, self-consumption reaches 50%-80%. As a result, you will be more independent from energy suppliers and be able to better utilize your capacity while saving on electricity costs.
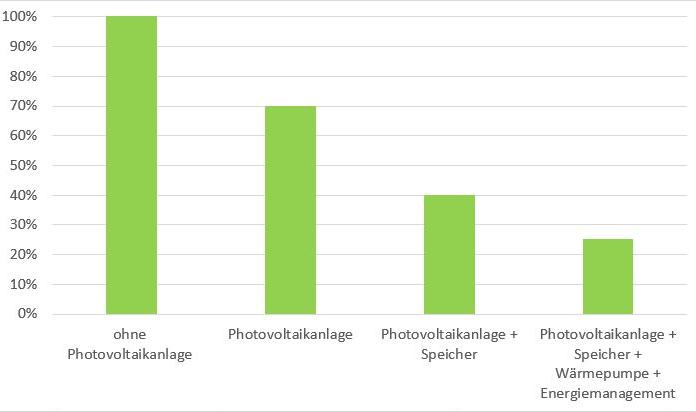
Power supply changes when installing photovoltaic systems and energy storage power supplies
Can power storage save more C02?
With power storage, less power is drawn from the grid. Electricity is only about 50% to 60% renewable energy, while solar panels can produce 100% renewable energy. So with power storage you always save CO2.
Electrical storage produces CO2 emissions only during the production process. The Heidelberg Institute for Energy and Environmental Research estimates that producing 1 kilowatt hour (kWh) of storage capacity will release approximately 125 kilograms of carbon dioxide. This number is expected to decline further as technology advances. Each kilowatt hour of electricity produces about 420 grams of carbon dioxide, and each kilowatt hour is not obtained from the grid but from electricity storage, so 420 grams of carbon dioxide is saved, so the carbon dioxide released during the production process is usually available within one to two years. compensate.
Example: CO2 balance of 8kWh battery storage, 4000 kWh household electricity consumption
For a typical 8kWh battery storage for a home, assuming a storage capacity of 125kg per kWh, approximately 1,000kg of CO2 will be released during production. Assuming an electricity demand of 4,000 kWh, 8 kWh of electricity storage to increase self-consumption from 30% to 65% would require 1,400 kWh of electricity from the electricity supplier. Since one kilowatt-hour of electricity produces approximately 420 grams of carbon dioxide, over a year this saves over 588 kilograms of carbon dioxide. After 1.7 years, manufacturing emissions have reached equilibrium. The carbon dioxide emission reduction over 20 years is 11.7 tons.
CO2 emitted by producing an 8 kWh storage: 8 x 125 kg = 1,000 kg
Reduced electricity supply through photovoltaic system without electricity storage:4000 kWh x 0.30 = 1200 kWh
Reduced power supply via memory:4000 kWh x 0.65 = 2600 kWh
Additional current savings through power storage:2,600 kWh - 1,200 kWh = 1,400 kWh
Annual CO2 savings from electricity storage:1,400 x 0.420 kg = 588 kg
Year before offsetting CO2 emissions:1000kg/588kg=1.7
CO2 emission reduction 20-year operating life= 588 kg x 20 – 1,000 = 11.7 tons of CO2


